The Soviet Union, officially known as the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a colossal entity that existed from 1922 until its dissolution in 1991. This vast territory spanned multiple time zones and encompassed a diverse array of cultures, languages, and histories. Understanding the map of Soviet Union countries is essential for grasping the geopolitical landscape of Eastern Europe and Central Asia, both during the Soviet era and in its aftermath. In this article, we will delve into the various countries that were once part of the Soviet Union, exploring their historical significance and contemporary relevance. This exploration will provide a comprehensive understanding of the legacy left by the USSR and its impact on the world today.
Throughout this article, we will examine the individual countries that emerged from the Soviet Union's dissolution, their geographical locations, and their evolution since gaining independence. By analyzing the map of Soviet Union countries, we will also uncover the socio-political dynamics that shaped the region and continue to influence international relations. Additionally, we will highlight key statistics and facts that underscore the importance of this topic in the context of global history.
Whether you are a history enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about the former Soviet states, this article aims to provide valuable insights and a thorough understanding of the map of Soviet Union countries. Join us as we embark on this informative journey through time and geography.
Table of Contents
- Overview of the Soviet Union
- Countries Within the Soviet Union
- Geographical Distribution of Soviet States
- Political Legacy of the USSR
- Cultural Diversity in Soviet Republics
- Economic Impact Post-Soviet Union
- Current Relations Among Former Soviet States
- Conclusion
Overview of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formed in the aftermath of the Russian Revolution of 1917, which led to the establishment of a socialist state. Comprised of 15 republics, the USSR was a federation that sought to promote Marxist-Leninist principles. The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 was a pivotal moment in world history, marking the end of the Cold War and the emergence of independent nations from its former territory.
Countries Within the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union consisted of the following 15 republics, which later became independent countries:
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Estonia
- Georgia
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Russia
- Tajikistan
- Turkmenistan
- Ukraine
- Uzbekistan
- Moldova
- Lithuania
Each of these republics had its own unique history and cultural identity, contributing to the rich tapestry of the Soviet Union.
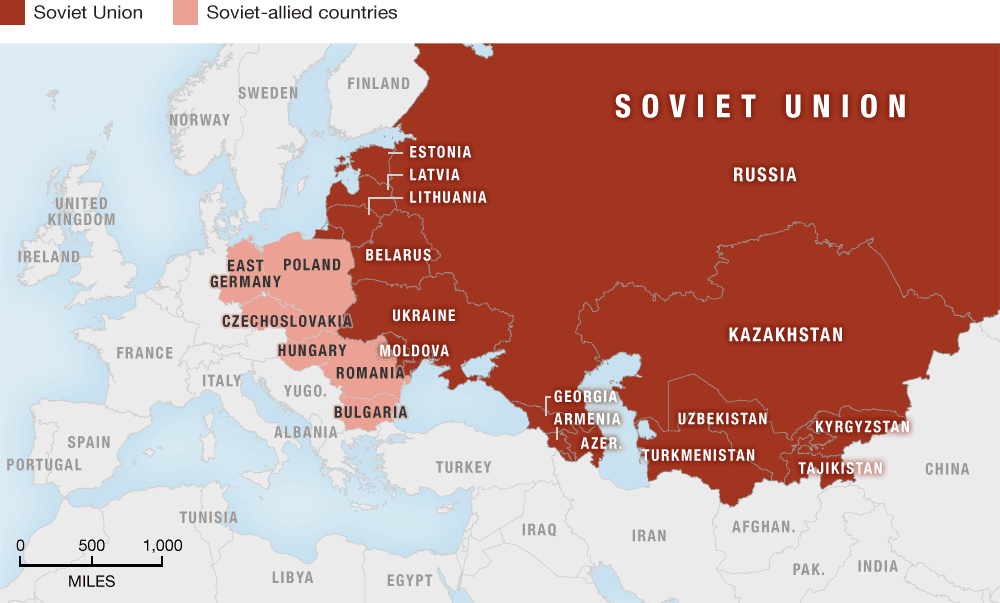
Geographical Distribution of Soviet States
The geographical distribution of Soviet states covers a wide area, stretching from Eastern Europe across Central Asia to the Arctic Circle. The map of Soviet Union countries highlights this vast expanse:
- Western Bloc: Comprising countries like Ukraine, Belarus, and the Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania), these nations share borders with several European countries.
- Caucasus Region: Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia are located in this region, known for its mountainous terrain and diverse cultures.
- Central Asia: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan make up this significant area, characterized by vast steppes and deserts.
- Eastern Europe: Russia spans a large portion of Eastern Europe and Northern Asia, making it the largest country in the world.
Map Overview
Below is a simplified representation of the map of Soviet Union countries:

Political Legacy of the USSR
The political legacy of the Soviet Union continues to influence global politics. The ideological battle between capitalism and communism defined much of the 20th century. The dissolution of the USSR led to the emergence of multiple political systems in the former republics, ranging from democratic governance to authoritarian regimes. Understanding the political evolution of these countries is crucial for analyzing contemporary geopolitical dynamics.
Cultural Diversity in Soviet Republics
The cultural diversity within the Soviet republics was one of the defining characteristics of the USSR. Each republic had its own language, traditions, and customs. This rich cultural heritage is evident in various aspects:
- Language: Over 100 languages were spoken across the Soviet Union, reflecting its ethnic diversity.
- Religion: The USSR was home to various religious groups, including Orthodox Christians, Muslims, and Jews.
- Art and Literature: Each republic contributed to the arts, producing renowned writers, artists, and musicians.
Economic Impact Post-Soviet Union
The economic impact of the Soviet Union's dissolution was profound. Many former Soviet states faced significant challenges as they transitioned from centrally planned economies to market-oriented systems. The following points highlight the economic transformations:
- Privatization: Many state-owned enterprises were privatized, leading to varying degrees of success.
- Economic Disparities: There are significant economic disparities between the former Soviet republics, with some achieving rapid growth while others struggled.
- Integration Challenges: Efforts to integrate economies have been met with both collaboration and conflict among the former republics.
Current Relations Among Former Soviet States
The relationships among former Soviet states are complex and multifaceted. While some nations maintain strong ties, others experience tensions due to historical grievances or geopolitical interests. Key aspects of current relations include:
- Regional Organizations: The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) are examples of attempts to foster cooperation.
- Geopolitical Rivalries: Ongoing disputes, such as the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, highlight enduring tensions.
- Economic Partnerships: Countries like Kazakhstan and Belarus have sought closer economic ties with Russia, while others pursue integration with the West.
Conclusion
In summary, the map of Soviet Union countries provides a fascinating lens through which to understand a significant period in world history. The legacy of the USSR is evident in the political, cultural, and economic landscapes of the former republics. As we reflect on this intricate history, it is crucial to remain informed about the ongoing developments in these nations. We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments, explore related articles, and continue your journey of discovery about this captivating topic.
Thank you for reading! We hope you found this article informative and engaging. Please visit us again for more insights and articles on history and geopolitics.